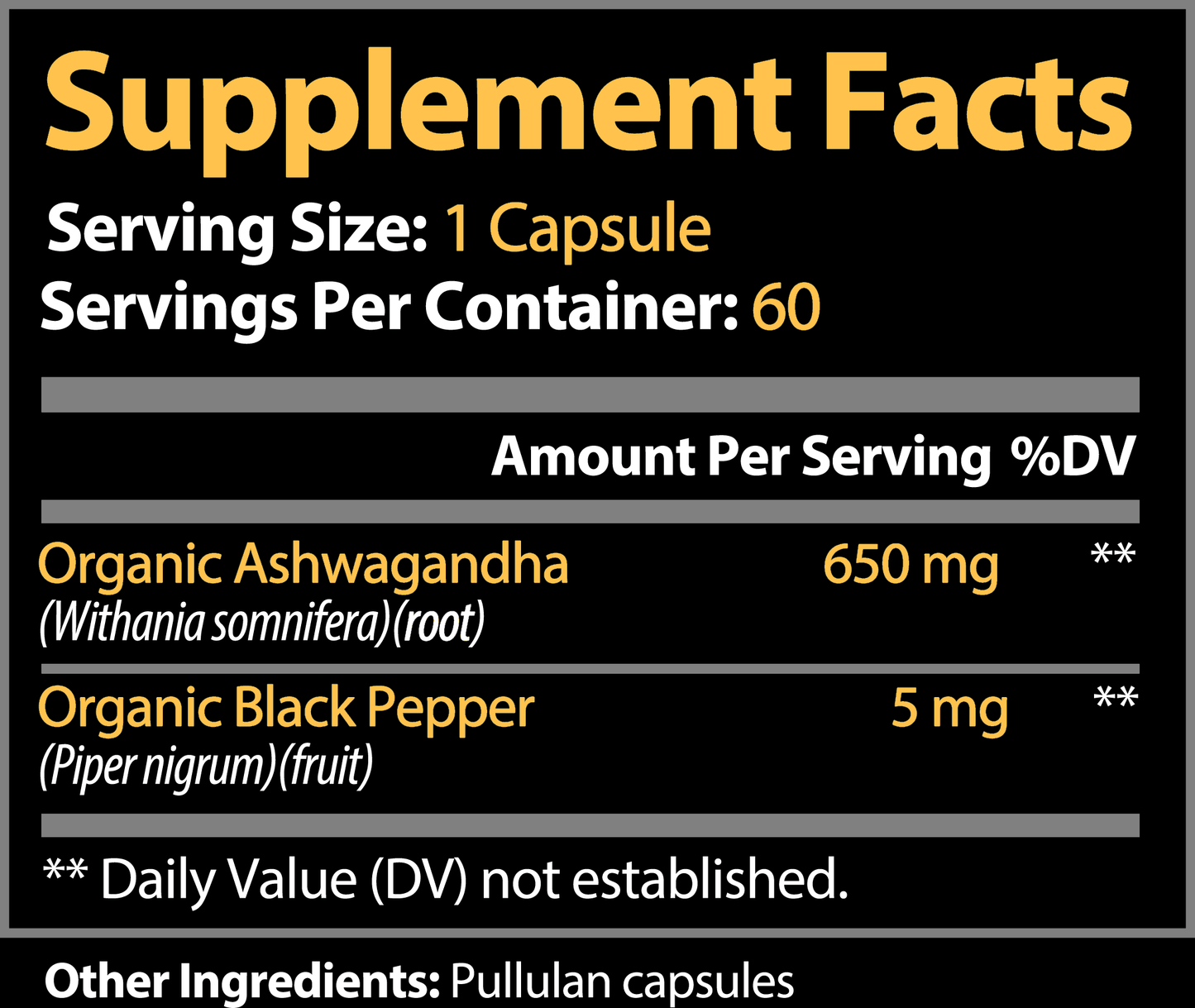
Ashwagandha for 🧠Cognitive Boost & Well-Being
Share
In today's fast-paced world, keeping your brain sharp is essential.
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a powerful ancient herb and a popular adaptogenic natural remedy that has been used as a key herb in Ayurvedic medicine for over 3000 years to promote overall well-being and improve various aspects of health.
Based on deep scientific research, this ancient herb shows promise in boosting memory, focus, and overall mental performance.
Here's what recent studies reveal about Ashwagandha's impact on cognitive health.

🧪 Active Compounds of Ashwagandha
Most of the biological activities of W. somnifera have been attributed to two key steroidal lactones — withanolides.
In addition, bioactive constituents such as withanosides, alkaloids, flavonoids, and sitoindosides are also present with a broad spectrum of therapeutic potential.
![Infographic detailing the various classes of bioactive compounds present in Ashwagandha, displayed in a multi-column format with category headers and specific compounds listed under each. Categories and examples include: Alkaloids: Ashwagandhine, Isopelletierine, Pseudotropine, [3]-Tigloyloxytropine, Tropeltioglate, Dlisopelletierine, Hygrine, Mesoanaferine, Choline, Somniferine, Withanine, Withananine, Hentriacontane, Visamine, Withasomnine, Somniferinine, Somnininine, Nicotine, Cuscoyhygrine, Pseudotropin, Anahygrine, Anaferine, Tropine. Steroidal lactones: Withanolide – A, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M; Withaferin – A; Withanone; Withasomidienone; Withaferin A; Withanolides A–Y; Withanone; Withasomniferin – A; Withasomniferols A–C. Steroids: Ergostane, Cholesterol, Sitoindosides IX, X, Diosgenin, Stigmastadien, Stigmasterol, β–sitosterol. Flavonoids: Quercetin, 7-hydroxyflavone, Kaempferol. Phenolics: Coumaric Acid, Caffeic Acid, Chlorogenic Acid, Gallic Acid, Ferulic Acid, Catechin. Saponins: Sitoindoside VII, Sitoindoside VIII. Glycosides: Withanosides I–VII, Withanamides. Others: Tannins, resin, fatty acids, organic acids, amino acids. On the right side, a photograph shows rows of Ashwagandha plants growing in soil under natural sunlight.](https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0750/6106/8084/files/Various_classes_of_bioactive_compounds_present_in_Ashwagandha_BIOHQ.jpg?v=1744444111)
Various classes of bioactive compounds present in Ashwagandha (adapted from Gaurav, H. et al., 2023)
🔬 Mechanisms of Action
Stress Management🧘
Ashwagandha is classified as an adaptogen, meaning it modulates stress hormone (cortisol) levels, which, in turn, calms the nervous system and improves cognition. [2, 3, 4]

Changes in Hormone levels after 60 days of 240 mg Ashwagandha extract intake (adapted from Lopresti, A. L. et al., 2019)
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects🍀
The plant's antioxidant compounds help combat oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals. [5, 6]
Withanolides in Ashwagandha exhibit anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines. [7, 8]
Both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects can support brain health by reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the brain cells — neurons.

Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory effects of Ashwagandha (adapted from Guo, S. et al., 2024)
Neuroprotective Effects🧠
Also, studies on animals and cell cultures have shown that Ashwagandha-root extract can promote a neuroprotective effect not only via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, but also directly by supporting neuronal health. [9, 10, 11]
📋 Human studies
4 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies on healthy adults [12, 13, 14, 15] and 1 the same design study on adults with mild cognitive impairment [16] have shown that Ashwagandha can provide significant improvements in cognitive functions:
- Treatment with one Ashwagandha SR capsule once daily for 90 days improved memory and focus, psychological well-being, and sleep quality, reduced stress levels, and was safe and well-tolerated. [12]
- ...significant differences were observed in cognitive flexibility, reaction time, psychomotor speed, and executive functioning, in which the Ashwagandha groups out-performed the placebo group. [13]
- Acute supplementation with 400 mg of ashwagandha improved selected measures of executive function, helped sustain attention, and increased short-term/working memory. [14]
- ...ashwagandha supplementation (225 mg) may improve some measures of memory, attention, vigilance, and executive function while decreasing perceptions of tension and fatigue in younger healthy individuals. [15]
- Ashwagandha may be effective in enhancing both immediate and general memory in people with MCI (mild cognitive impairment), as well as improving executive function, attention, and information processing speed. [16]
Conclusion
Scientific evidence supports the use of Ashwagandha as a potent tool for supporting brain health and cognitive function 🧠